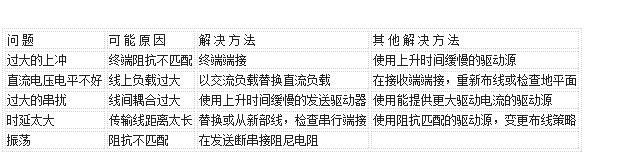
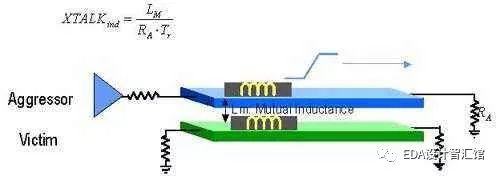
1. What is electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)? (Electromagnetic Interference), there are two kinds of conducted interference and radiated interference. Conducted interference refers to the coupling (interference) of signals on one electrical network to another electrical network through a conductive medium. Radiated interference refers to the interference source coupling (interference) its signal to another electrical network through space. In high-speed PCB and system design, high-frequency signal lines, integrated circuit pins, various connectors, etc. may become radiation interference sources with antenna characteristics, which can emit electromagnetic waves and affect other systems or other subsystems in the system. normal work. Since the emergence of noise reduction technology in electronic systems in the mid-1970s, it is mainly due to the US Federal Communications Commission in 1990 and the European Union in 1992 proposed regulations on commercial digital products. These regulations require companies to ensure that their products comply with strict magnetic susceptibility. And launch guidelines. Products that comply with these regulations are called EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility). 2. What is signal integrity? Signal integrity refers to the quality of the signal on the signal line. A signal with good signal integrity means that it has the necessary voltage level value when needed. Poor signal integrity is not caused by a single factor, but by multiple factors in board-level design. The main signal integrity problems include reflection, oscillation, ground bounce, crosstalk, etc. Common signal integrity problems and solutions 3. What is reflection? Reflection is the echo on the transmission line. Part of the signal power (voltage and current) is transmitted to the line and reaches the load, but part is reflected. If the source and load have the same impedance, reflection will not occur. The impedance mismatch between the source and the load will cause line reflections, and the load will reflect part of the voltage back to the source. If the load impedance is less than the source impedance, the reflected voltage is negative. Conversely, if the load impedance is greater than the source impedance, the reflected voltage is positive. Variations in factors such as wiring geometry, incorrect wire termination, transmission through connectors, and discontinuities in the power plane can all cause such reflections. 4. What is crosstalk? Crosstalk is the coupling between two signal lines. The mutual inductance and mutual capacitance between the signal lines cause noise on the line. Capacitive coupling induces coupling current, and inductive coupling induces coupling voltage. The parameters of the PCB layer, the signal line spacing, the electrical characteristics of the driving end and the receiving end, and the line termination method all have a certain impact on the crosstalk. 5. What are overshoot and undershoot? Overshoot is the first peak or valley that exceeds the set voltage-for rising edges it means the highest voltage and for falling edges it means the lowest voltage. Undershoot refers to the next valley or peak. Excessive overshoot can cause the protection diode to work, leading to premature failure. Excessive undershoot can cause false clock or data errors (misoperation). 6. What are ringing and rounding? The phenomenon of ringing is repeated overshoot and undershoot. Signal oscillation and surrounding oscillation are caused by excessive inductance and capacitance on the line. The oscillation belongs to the under-damped state and the surrounding oscillation belongs to the over-damped state. Signal integrity problems usually occur in periodic signals, such as clocks. Oscillation and surround oscillation are caused by many factors like reflection. Oscillation can be reduced by proper termination, but it is impossible to completely eliminate it. 7. What is ground plane bounce noise and return noise? When there is a large current surge in the circuit, it will cause ground plane bounce noise (referred to as ground bounce). If a large number of chip outputs are turned on at the same time, there will be a larger one. The transient current flows through the power plane of the chip and the board. The inductance and resistance of the chip package and the power plane will cause power noise, which will produce voltage fluctuations and changes on the real ground plane (0V), and this noise will affect Actions of other components. The increase of load capacitance, the decrease of load resistance, the increase of ground inductance, and the increase of the number of switching devices at the same time will all cause the increase of ground bounce. Due to the division of the ground plane (including power and ground), for example, the ground plane is divided into digital ground, analog ground, shielding ground, etc. When the digital signal goes to the analog ground area, ground plane return noise will be generated. Similarly, the power layer may be divided into 2.5V, 3.3V, 5V, etc. Therefore, in the multi-voltage PCB design, the bounce noise and return noise of the ground plane require special attention. 8. What is the difference between time domain and frequency domain? Time domain is the process of voltage or current changes based on time, which can be observed with an oscilloscope. It is commonly used to find out the delays, skew, overshoot, undershoot, and settling times from pin to pin. The frequency domain is the process of voltage or current changes based on frequency, which can be observed with a spectrum analyzer. It is commonly used for comparison between waveforms and FCC and other EMI control limits. 9. What is impedance? Impedance is the ratio of the input voltage to the input current on the transmission line (Z0=V/I). When a source sends a signal to the line, it will prevent it from driving until 2*TD, the source does not see its change, where TD is the line delay (delay). 10. What is settling time? Settling time is the time required for an oscillating signal to stabilize to a specified final value. 11. What is the pin-to-pin delay? The pin-to-pin delay refers to the time between the change of the state of the driver and the change of the state of the receiver. These changes usually occur at 50% of the given voltage. The minimum delay occurs when the output first crosses the given threshold (threshold), and the maximum delay occurs when the output last crosses the voltage threshold (threshold). Measure all of these Happening. 12. What is skew? The skew of the signal is the time deviation between the same network reaching different receivers. The offset is also used for the time deviation of the clock and data arrival on the logic gate. 14. What is a quiescent line? It does not switch in the current clock cycle. Also called "stuck-at" line or static line. Crosstalk (Crosstalk) can cause a static line to switch within a clock cycle. 15. What is false clocking? False clocking means that the clock has crossed the threshold and changed the state unconsciously (sometimes between VIL or VIH). Usually caused by excessive undershoot or crosstalk. PS5 battery , PS5 controller batetry pack, PS5 controller battery 1500mAh,PS5 Rechargeable Battery ,Battery Pack for PS5 Dualsense Controller Shenzhen GEME electronics Co,.Ltd , https://www.gemesz.com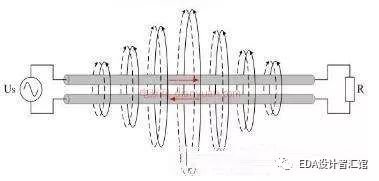



15 questions you have to know about high-speed design
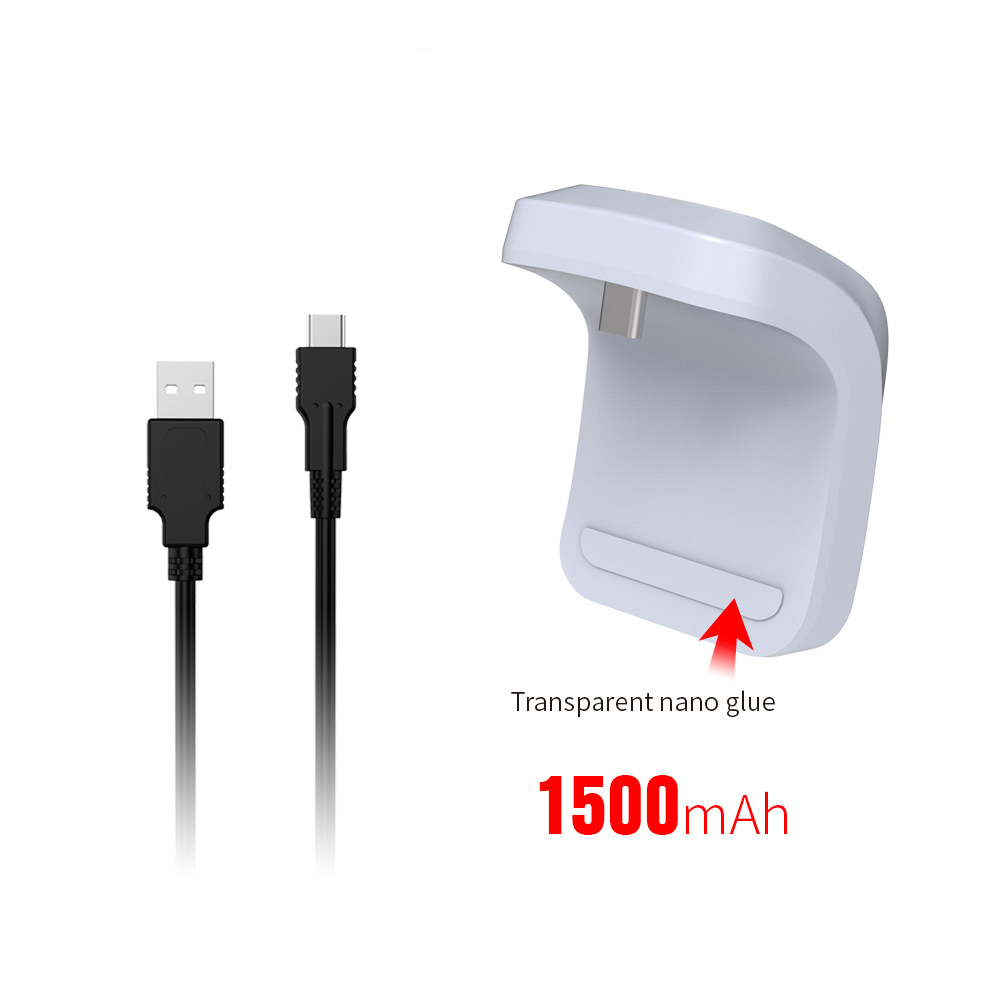
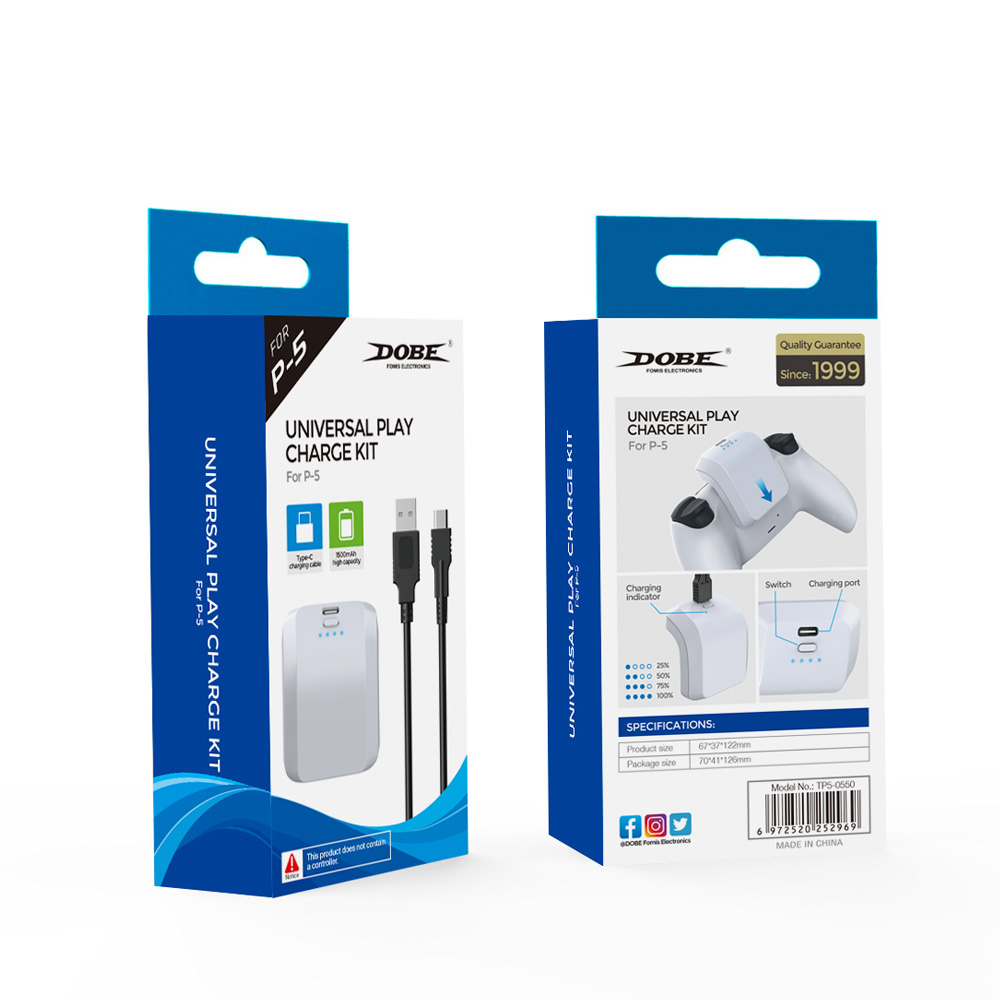
1. The battery capacity of this product is 1500mAh;
2. Charging current 560MA, fully charged time: about 3 hours;
3. When the battery pack is in the standby state, close all output ports and enter the sleep state. At this time, the product enters low power consumption to achieve the purpose of energy saving and environmental protection;
4.When the battery pack is in the standby state,the battery level of the built-in battery pack can be detected by the battery detection button. The battery detection indicator LED is detected from low to high, and then the battery indicator will automatically turn off after 30 seconds; or long press the battery detection button for 2 seconds to turn off .
5. In the charging state of the battery pack, the LED power indicator will check from low to high, and then the corresponding power value will be always on, indicating the current power of the battery pack. After the battery pack is fully charged, the four battery indicators will be always on; until it is unplugged the external
adapter ,then the 4 lights will off.
6. Battery pack charging method: first constant current, then constant voltage.
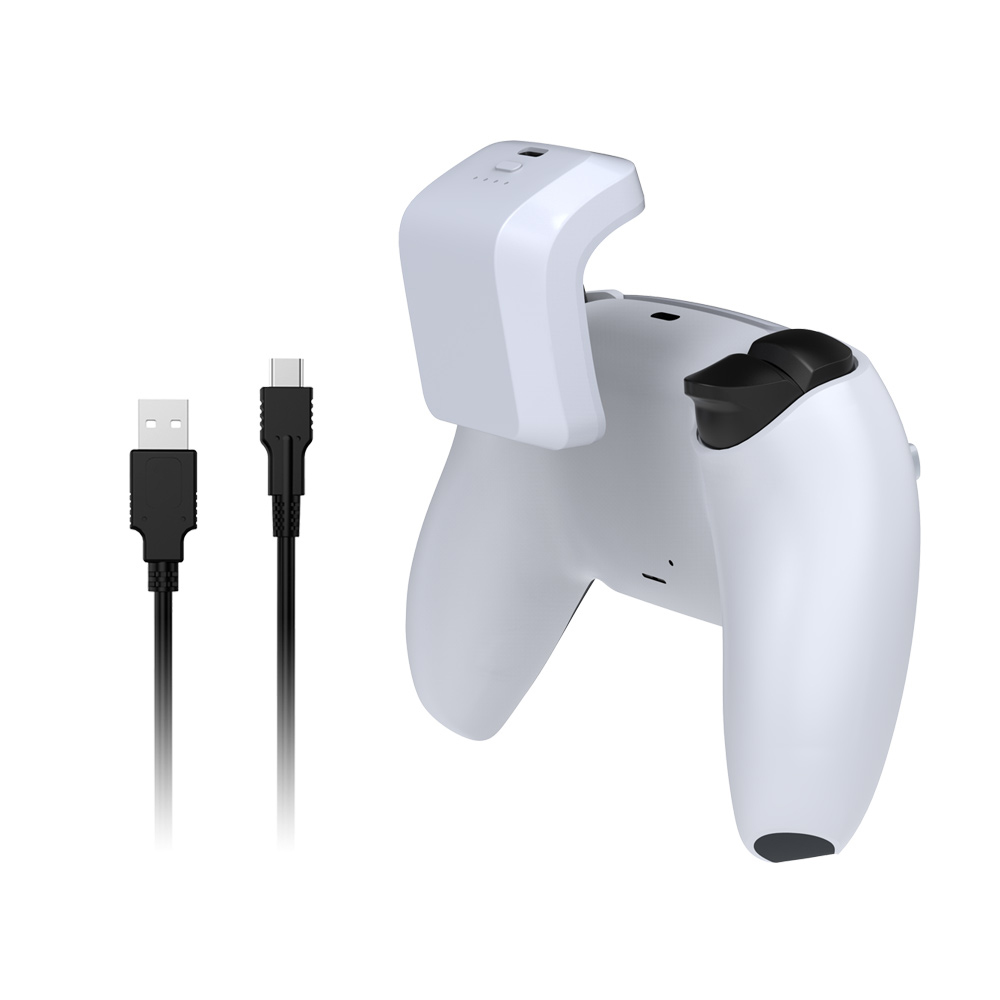
7. When the battery pack is charging the gamepad, the current battery indicator will always be on, and the number of LED lights that are always on represents the remaining battery power in the charging bag, which is convenient for you to know the power in the battery pack.
8. The battery power detection function is set inside the product. When the power of the battery pack continues to decrease as the gamepad is charged, and is below the normal discharge range of the charging bag, the first battery indicator LED flashes.quickly to indicate that it is charging and completely out of power When the time, the LED light goes out, and then the output port is closed to protect the battery inside the charging pack from over-discharge damage.
9. Output short-circuit protection:When the output port is short-circuited, the output voltage will be automatically turned off. To activate again, you need to recharge the battery pack to activate.
Product Name
1500mAh High Capacity Rechargeable Battery for PS5 Controller
weight
100g
Product size
67*37*122MM
Box size
70*41*126MM
Product color
black or OEM
Product package
Gift Box
OEM/ODM
warmly welcome
Advatage
100 QC test before shipping